Hexadecimal Number
Hexadecimal number system uses 16 different symbols to represent a numeric value. It uses numbers 0 to 9 and alphabets A to F for representation. . The place value of each digits of an hexadecimal number varies as the whole number powers of 16 starting from the right (Least Significant Digit). The first single digit number in hexadecimal system is 0 and the last is F. Similarly, the first two digit hexadecimal number is 10 and the last is FF and so on. It is used as an alternative for binary numbers by developers and programmers.
Gray code
Gray code, also known as reflected binary code, is a code having digits 0 and 1. Gray code do not have place value for its digits. Any successive codes in Gray code system have only one bit changes.
How to convert hexadecimal to gray code
Hexadecimal number cannot be directly converted to Gray code. Hence, to convert hexadecimal to gray code, first, convert the hexadecimal number to binary. Then, convert the binary to gray code.
Hexadecimal to gray conversion can be well understood from the following example:
Convert 1916 to gray code
Step 1: To Convert 1916 to gray code at first convert 1916 to binary.
To convert hexadecimal to binary write down the binary code corresponding to each digit of hexadecimal number.
| Hex | 1 | 9 |
| Decimal | 1 | 1001 |
Hence, 1916 = 110012
Read: How to convert hexadecimal to Binary
Step 2: Now, Convert 110012 to gray code.
The MSB (Most Significant Bit) of a gray code and binary code will be the same.
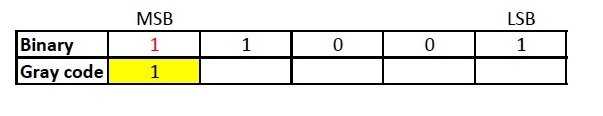
The next digit of gray code will be the EXOR of the MSB and the digit right to the MSB of the binary code.
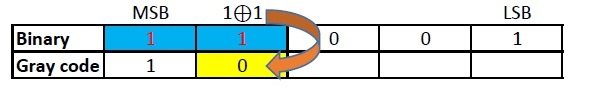
Similarly EXOR the digit in place and the previous digit of binary code to obtain the next digit of gray code
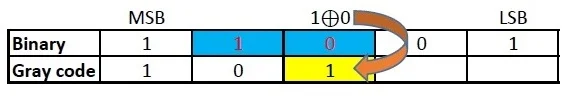
Repeat the previous step.
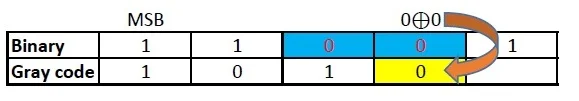
Repeat the previous step till the LSB of gray code is found.
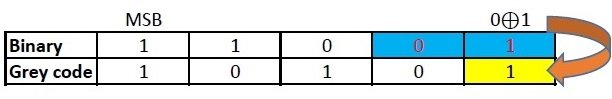
Therefore, Gray code corresponding to 1916 = 10101